Prerequisite
On the Zanata server you use
- Register a Zanata account and have a generated API key
- Create the project and version to use (configure your locales, permissions etc)
- Download the Zanata project version config, customize it if needed and check it into your SCM
Global Configuration in your Jenkins server
- Configure Zanata credentials (username and API key) in Jenkins Credentials view
- Configure Github credential or equivalent remote SCM credentials if you want to push commit
- JAVA_HOME defined as environment variable (You should install JDKs and then expose one's installation path as environment variable. This way the JAVA_HOME variable is correct both in master and in slave)
Next step
Configure a job to listen to Zanata webhook event
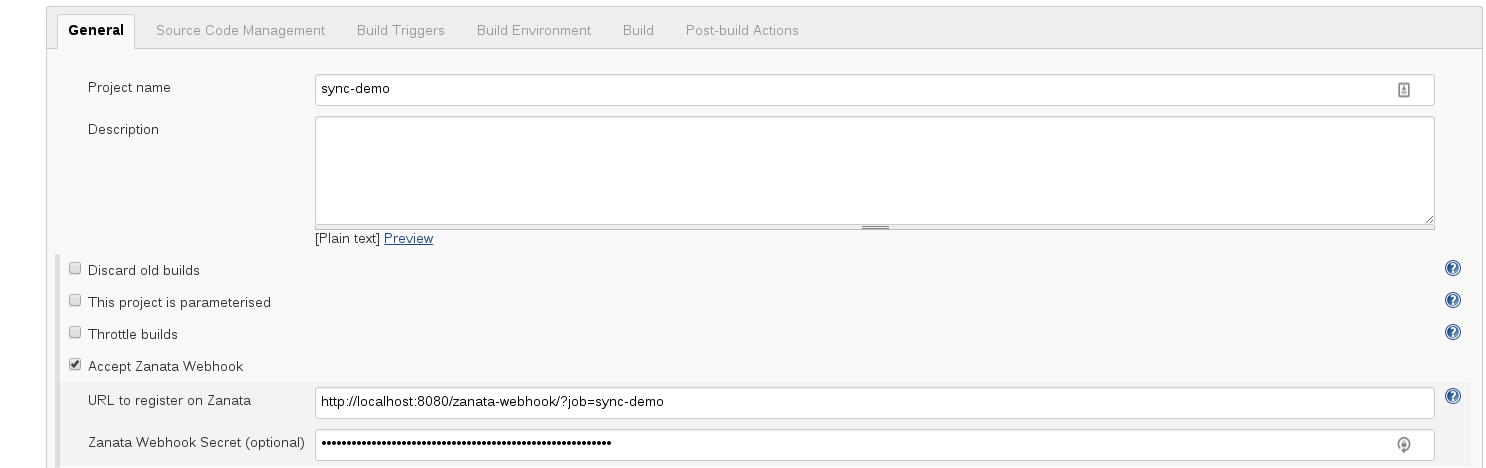
In your job configuration, check the Accept Zanata Webhook checkbox under
'General' section. It will open up more fields:
- The 'URL to register on Zanata' field is readonly for you to register your
webhook in Zanata. See Zanata webhook for more detail.
- The optional webhook secret field is for verification of incoming webhooks
Configure your SCM for your Jenkins job as usual. If you want to trigger a build when SCM changes, you can leverage other Jenkins plugins. e.g. Github plugin to listen to github webhook event and trigger a build to push resources to Zanata.
Then in the 'Build' section, you will have two options to push source to and/or pull translation from Zanata server.
- Use 'Zanata Sync' build step
- Install Zanata CLI on Jenkins node and use 'Zanata Sync via CLI' build step
Option 1 has the advantage of being installation free and simple to use. It will work on all type of jenkins slave nodes. It will commit translation after pull automatically if you use Git as SCM. Disadvantage being that it uses only the included version of Zanata CLI java classes. and you can't do much customization for push and pull.
Option 2 has the advantage of being flexible. You can use all the features and options of Zanata CLI. The disadvantage is, you will need to know how to use Zanata CLI. You also need to manually manage source control in your shell script.